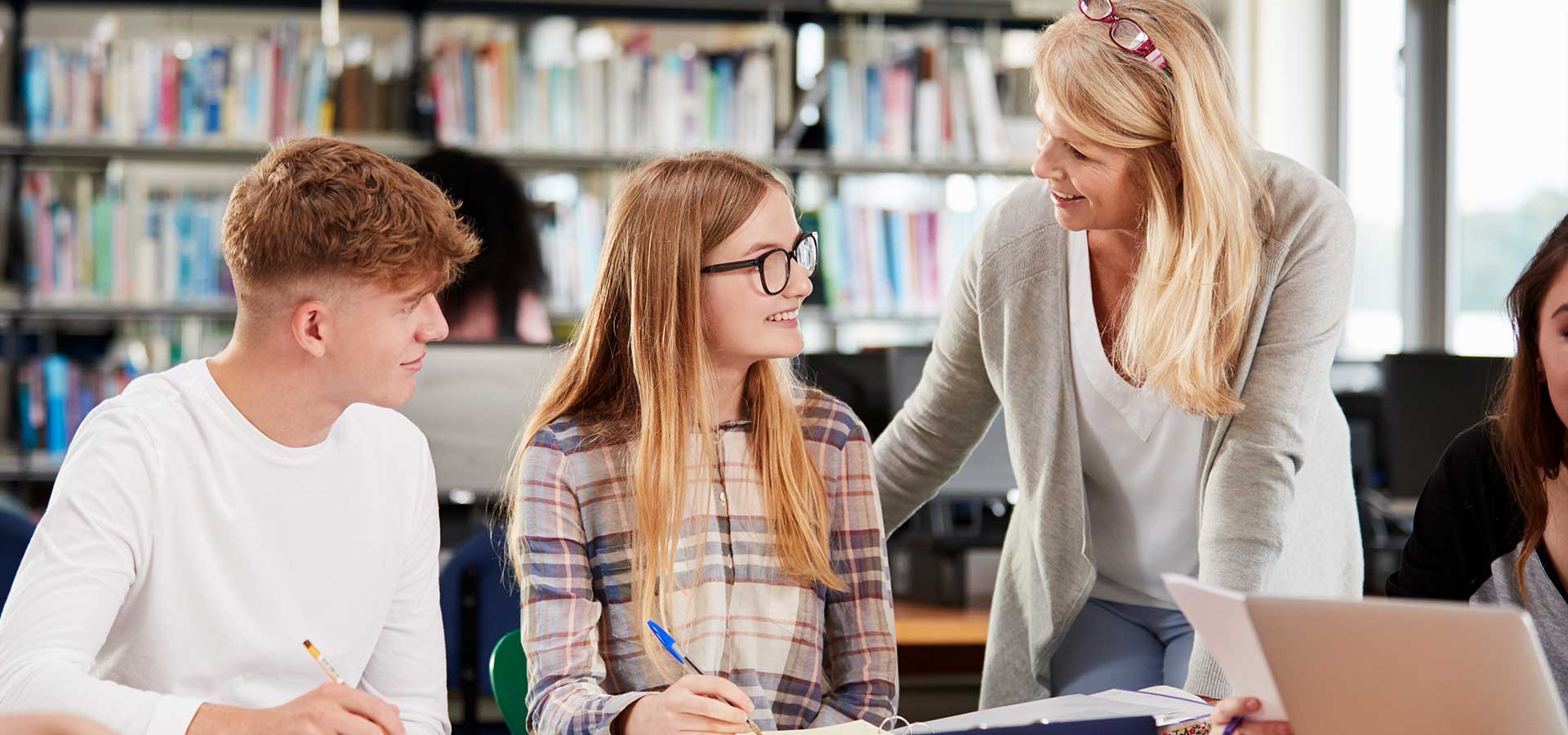
Educational Blog
Blog 1
Title: Insights & Ideas for Educational Excellence for ADHD:
By- Dr. Raghavendra Gowd M C , CEO
Personalized Learning Plans: Tailor education plans to accommodate different learning styles and attention spans characteristic of ADHD.
Multisensory Learning: Engage multiple senses (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) to enhance learning retention and engagement.
Structured Routine: Establish consistent schedules and routines to provide stability and predictability, which can help ADHD students stay focused.
Positive Reinforcement: Use rewards and positive reinforcement techniques to encourage desired behaviors and academic achievements.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate mindfulness practices and relaxation exercises to help manage stress and improve concentration.
Interactive and Hands-on Activities: Integrate interactive and hands-on learning activities to keep students actively engaged and interested.
Technology Integration: Utilize educational technology tools and apps designed to support ADHD learners, such as time-management apps and focus-enhancing software.
Collaboration with Parents and Teachers: Foster open communication and collaboration between parents, teachers, and support staff to create a cohesive support system for the student.
Skill Development: Focus on developing executive functioning skills like organization, planning, and time management through structured interventions.
Peer Support and Group Dynamics: Encourage peer support and group learning environments that promote social interaction and cooperative learning among ADHD students.
Implementing these strategies can create an inclusive and supportive educational environment that promotes success and well-being for students with ADHD.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Blog 2,
Title: Unlocking the Puzzle: Exploring Fascinating Facts About ADHD in Canada
By- Dr. Raghavendra Gowd M C , CEO
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals worldwide, including Canada. While ADHD is often discussed in terms of its challenges, there are also many intriguing aspects of this condition that shed light on its complexity and impact. Here, we delve into some fascinating facts about ADHD in Canada, offering insight into its prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment within the country.
Prevalence in Canada:
ADHD is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders diagnosed in Canada, affecting individuals of all ages. According to the Centre for ADHD Awareness, Canada (CADDAC), approximately 5-7% of children and adolescents in Canada are estimated to have ADHD. Additionally, ADHD is not limited to childhood; it can persist into adulthood, with prevalence rates ranging from 2-5% among adults.
Gender Differences:
In Canada, as in many other countries, there are notable gender differences in ADHD diagnosis. Historically, boys have been diagnosed with ADHD at a higher rate than girls. However, recent research suggests that this gender gap may be narrowing, with growing recognition of ADHD in females. Despite this progress, there is still a need for greater awareness and understanding of how ADHD manifests in girls and women, as their symptoms may differ from those typically observed in boys.
Impact on Education and Employment:
ADHD can have significant implications for education and employment outcomes in Canada. Children and adolescents with ADHD may experience academic difficulties, including challenges with attention, organization, and impulse control. In adulthood, individuals with ADHD may encounter obstacles in the workplace, such as difficulty maintaining focus, meeting deadlines, and managing time effectively. However, with appropriate support and accommodations, many individuals with ADHD can thrive academically and professionally.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for ADHD in Canada typically involves a multimodal approach, combining medication, psychotherapy, and behavioral interventions. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamine-based drugs, are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms of ADHD. However, non-pharmacological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and organizational skills training, are also recommended to address the functional impairments associated with ADHD.
By understanding the prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment of ADHD within the Canadian context, we can work towards improving access to resources and support for individuals affected by this condition. Through continued research, advocacy, and education, we can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with ADHD, empowering them to reach their full potential and lead fulfilling lives.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Blog 3,
Title: Innovating Education for ADHD and Learning Disability Students
By- Dr. Raghavendra Gowd M C , CEO
In today’s educational landscape, it’s crucial to explore innovative approaches that cater specifically to students with ADHD and learning disabilities. These students often face unique challenges that require tailored educational strategies to optimize their learning experiences and outcomes.
Understanding the Challenges
ADHD and learning disabilities can impact various aspects of a student’s academic journey. Challenges may include difficulty sustaining attention, organizing tasks, managing time effectively, and processing information. These hurdles can hinder their ability to thrive in traditional classroom settings.
Innovative Strategies in Education
1. Personalized Learning Plans
Implementing personalized learning plans is key to accommodating the diverse needs of students with ADHD and learning disabilities. These plans can include:
Individualized Instruction: Tailoring teaching methods to match the student’s learning style and pace.
Flexible Learning Environments: Offering options for alternative seating arrangements, quiet areas for concentration, and varied instructional formats (e.g., visual aids, hands-on activities).
Technology Integration: Utilizing educational apps and tools that provide interactive learning experiences and assistive technologies tailored to individual needs.
2. Multisensory Approaches
Engaging multiple senses (visual, auditory, tactile) can enhance learning retention and engagement for students with ADHD and learning disabilities. Techniques may involve:
Hands-on Learning: Incorporating manipulatives and interactive materials to reinforce concepts.
Visual Learning Aids: Using charts, diagrams, and videos to supplement verbal instructions.
Auditory Supports: Providing recorded lectures or audio texts to accommodate different learning preferences.
3. Executive Functioning Skills Development
Targeting executive functioning skills, such as organization, planning, and self-regulation, is crucial for academic success. Strategies include:
Structured Routines: Establishing predictable schedules and clear expectations to promote consistency and reduce anxiety.
Goal Setting: Helping students break down tasks into manageable steps and set achievable goals. Time Management Techniques: Teaching strategies for prioritizing tasks, estimating time needed for assignments, and using timers or reminders.
4. Collaborative Learning and Support Systems
Promoting a collaborative learning environment fosters peer support and social interaction, which are beneficial for students with ADHD and learning disabilities. Initiatives may include:
Peer Tutoring: Pairing students to work together and support each other’s learning.
Parent and Teacher Partnerships: Facilitating open communication to align strategies and support systems between home and school.
Future Directions
As we continue to innovate in education for ADHD and learning disability students, ongoing research and collaboration are essential. By leveraging technology, embracing diverse learning modalities, and prioritizing individualized support, we can create inclusive educational environments where all students can thrive.
In conclusion, the journey towards educational innovation for students with ADHD and learning disabilities requires dedication, creativity, and a commitment to meeting their unique needs. By implementing these innovative strategies and fostering a supportive community, we can empower these students to achieve their full potential and contribute meaningfully to society.
Let’s continue to push boundaries and pave the way for a more inclusive and equitable education system for all
Quick Links
Address & Contact
Registered Address:
British Columbia: READ HELP TECHNOLOGIES INC
C/O Tacenda Capital (VCC) INC.
Water Front Business Centre 145
Chadwick CT #220
North Vancouver
BC V7M 3K2 Canada.
Communication Address:
9866 132 Street Surrey BC V3T3S6 Canada.
Ontario Branch: READ HELP TECHNOLOGIES INC
C/O CEEJAL ENTERPRISES INC. O/A SANDALWOOD CARE PHARMACY, 10510 Torbram Road, Unit D&E, Brampton, Ontario, L6R 3N9, Canada.
Call Us : +1 (778) 951-1717
E-mail : info@readbest.ca
Copyright 2024 © All Right Reserved by Read Help Technologies Inc